Intel’s Open Image Denoise library has been recognized with a Technical Achievement Award by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences. This open-source tool, designed to reduce noise in ray-traced images using AI techniques, is integral to various rendering workflows in the film industry. The award acknowledges the library’s role in advancing digital image processing methods in cinematic production. Though not widely known outside professional visual effects and animation circles, it is crucial for pipelines requiring image clarity and rendering precision.
The Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences has recognized Intel’s Open Image Denoise library with a Technical Achievement Award. This open-source tool, developed to assist with the process of reducing noise in ray-traced images through AI techniques, has found a place in various rendering workflows within the film industry.
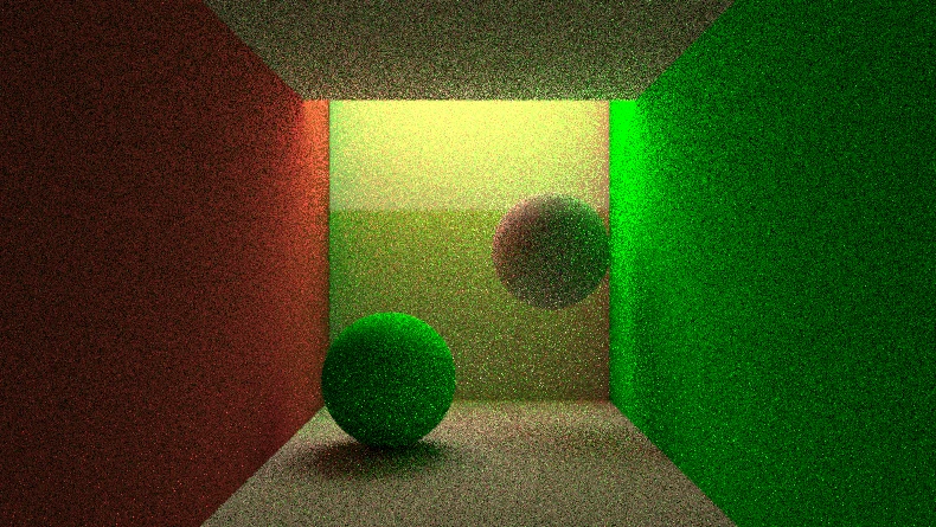
According to the Academy, the award acknowledges the library’s role in advancing digital image processing methods used in cinematic production. Though not widely known outside professional visual effects and animation circles, the tool has been incorporated into pipelines where image clarity and rendering precision are essential. The Academy, best known for organizing the annual Oscars ceremony, periodically selects such technologies for their influence on filmmaking practices and their usefulness in evolving industry standards.
Ray tracing has been well established as the basis for contemporary rendering. However, it demands substantial computational resources. When employed independently to create images devoid of noise and artifacts, a significant number of rays must be traced, which can be both slow and costly. However, by utilizing a sophisticated denoiser such as Intel’s Open Image Denoise, rendering times can be considerably shortened by enhancing the renderer, allowing for fewer rays to be traced without compromising image quality.
Intel Open Image Denoise addresses the issue of unwanted noise inherent to ray tracing through the application of AI neural networks. This process can accelerate real-time previews during the creative workflow and reduce the time required for final rendering. The library is a C/C++ API that facilitates its integration into most existing or new rendering solutions. And, a wide range of vendors have adopted it, with optimizations for various major CPU and GPU architectures from Intel, AMD, Nvidia, Apple, and Arm.
Intel Open Image Denoise is included in the Intel’s Rendering Toolkit and is distributed under the Apache 2.0 license. Its core technology is based on U-Net architecture, which is efficient and maintains details, thereby improving the quality of computer-generated imagery across the industry. As the library is open source and free to use, it comes with a training tool kit that enables users to develop custom denoising models using their own datasets, offering greater flexibility and enhanced image quality. Additionally, users have the option to retrain the provided denoising neural networks to suit their own renderers, styles, and films.
The library is also incorporated into numerous well-known rendering tools, such as Autodesk Arnold, Blender, Chaos V-Ray, Chaos Corona, Foundry Modo, Maxon Cinema 4D, among others.
The Scientific and Technical Awards were introduced in 1931 to recognize the achievements in science and technology’s critical role in advancing motion-picture production. The Academy honored scientific and technical achievements at the annual Scientific and Technical Awards ceremony on April 29. See the other 2025 SciTech recipients here.
LIKE WHAT YOU’RE READING? INTRODUCE US TO YOUR FRIENDS AND COLLEAGUES.